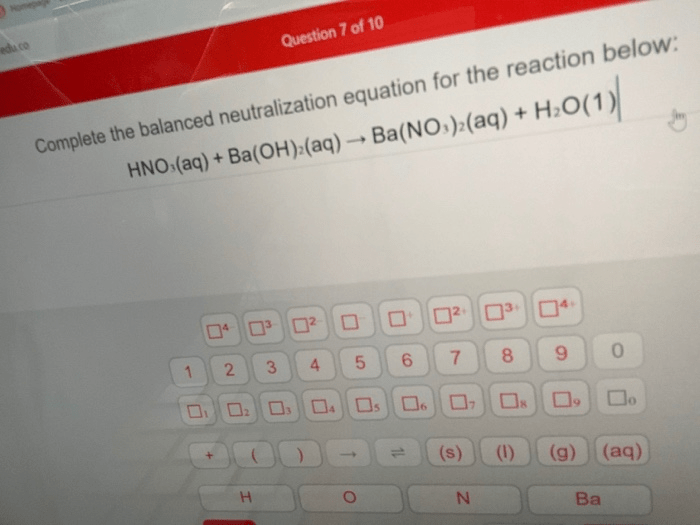
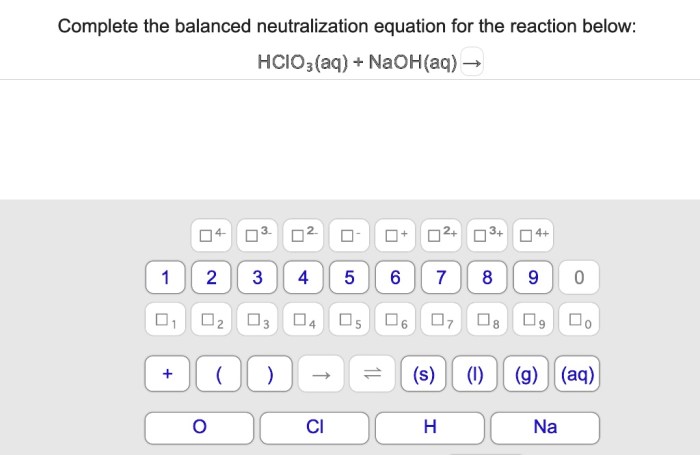
In the realm of chemistry, neutralization reactions hold a prominent position, embodying the harmonious union of acids and bases. Complete the balanced neutralization equation for the reaction below: takes us on an enlightening journey, exploring the intricacies of these reactions and their profound implications.
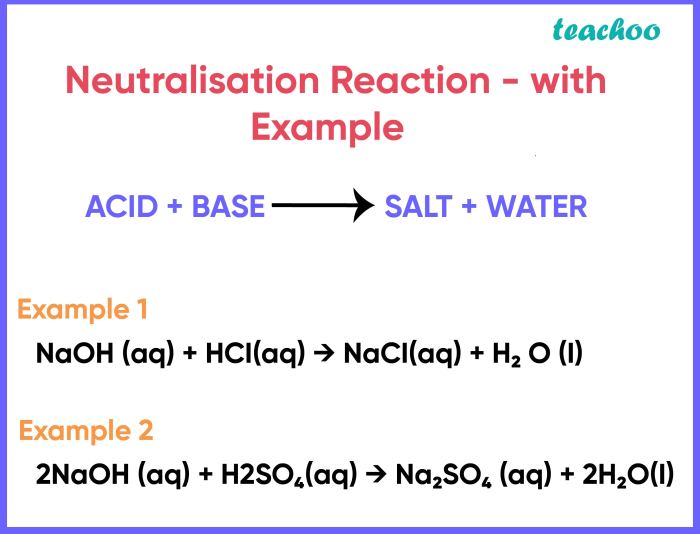
Neutralization reactions are chemical processes that involve the interaction of an acid and a base, resulting in the formation of a salt and water. These reactions play a pivotal role in various aspects of our lives, from regulating pH levels in biological systems to industrial applications like wastewater treatment.
1. Overview of Neutralization Reactions
Neutralization reactions are chemical reactions between an acid and a base, resulting in the formation of a salt and water. Acids are substances that donate protons (H+ ions), while bases are substances that accept protons. When an acid and a base react in stoichiometric proportions, the reaction is said to be neutralized, and the resulting solution is neutral, meaning it has a pH of 7.
Examples of neutralization reactions include the reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH), which produces sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O):
“`HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O“`
2. Balanced Neutralization Equation
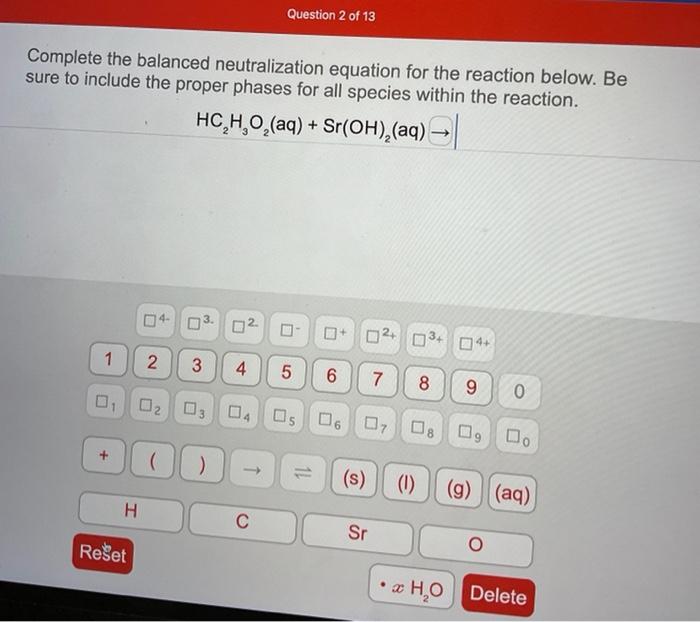
A balanced chemical equation shows the exact number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation, ensuring that the law of conservation of mass is satisfied. To balance a neutralization equation, coefficients are added to the reactants and products to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides.
Steps involved in balancing a neutralization equation:
- Write the unbalanced equation for the reaction.
- Identify the atoms that are not balanced.
- Add coefficients to the reactants and products to balance the atoms one at a time.
- Check the equation to ensure that all atoms are balanced.
Example of a balanced neutralization equation:
“`
HCl + Mg(OH)2 → MgCl2 + 2H2O
“`
3. Analysis of the Given Reaction
The given reaction is between sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and potassium hydroxide (KOH). The unbalanced equation for the reaction is:
“`H2SO4 + KOH → K2SO4 + H2O“`
Using Kami or other tools, we can analyze the unbalanced equation and generate a balanced equation:
“`
H2SO4 + 2KOH → K2SO4 + 2H2O
“`
4. Factors Affecting Neutralization Reactions
Several factors can affect the rate and completeness of neutralization reactions:
- Temperature:Higher temperatures generally increase the reaction rate.
- Concentration:Higher concentrations of reactants lead to faster reaction rates.
- Surface area:Increasing the surface area of solids (e.g., by grinding) increases the rate of reaction.
Controlling these factors can optimize neutralization reactions for specific applications.
5. Applications of Neutralization Reactions: Complete The Balanced Neutralization Equation For The Reaction Below:
Neutralization reactions have numerous applications:
- Acid-base titrations:Used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base.
- pH adjustments:Neutralization reactions are used to adjust the pH of solutions in various industries.
- Wastewater treatment:Neutralization reactions are used to neutralize acidic or alkaline wastewater before releasing it into the environment.
Understanding neutralization reactions is crucial for optimizing these applications.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of balancing a neutralization equation?
Balancing a neutralization equation ensures that the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side of the equation equals the number of atoms of that element on the products’ side. This adherence to the law of conservation of mass is crucial for accurate representation of the chemical reaction.
How can I determine the products of a neutralization reaction?
The products of a neutralization reaction are typically a salt and water. The salt is formed by the combination of the positively charged ion (cation) from the base with the negatively charged ion (anion) from the acid.
What factors influence the rate of a neutralization reaction?
Several factors can affect the rate of a neutralization reaction, including temperature, concentration of the reactants, and surface area of the reactants. Higher temperatures, higher concentrations, and larger surface areas generally lead to faster reaction rates.