What can cause your exhaust system to deteriorate over time? The answer to this question is complex and involves a variety of factors, including environmental conditions, driving habits, and the age of the vehicle. In this article, we will explore the most common causes of exhaust system deterioration and provide tips on how to prevent or minimize damage.
Some of the most common causes of exhaust system deterioration include:
1. Rust and Corrosion
Rust, the common term for iron oxide, is a major cause of exhaust system deterioration. It forms when iron or steel components in the exhaust system are exposed to moisture and oxygen, leading to a chemical reaction that produces rust.
This reddish-brown substance weakens metal components, making them more susceptible to cracking, leaking, and eventual failure.
Environmental Factors Accelerating Corrosion, What can cause your exhaust system to deteriorate over time
- Humidity and Moisture:High levels of humidity and frequent exposure to moisture accelerate the rusting process. Rain, snow, and even condensation can create an environment conducive to corrosion.
- Road Salt:Salt used for de-icing roads during winter can significantly increase the risk of corrosion. It creates a highly corrosive environment that attacks the metal components of the exhaust system.
- Exposure to Chemicals:Exhaust systems are exposed to various chemicals, including cleaning agents and fumes from gasoline and diesel fuel. These chemicals can react with the metal, leading to corrosion and other damage.
Preventing and Mitigating Rust Damage
- Regular Cleaning:Regularly cleaning the exhaust system removes dirt, debris, and road salt, reducing the risk of corrosion.
- Protective Coatings:Applying protective coatings, such as paint or anti-corrosion sprays, can create a barrier between the metal and moisture, preventing rust formation.
- Galvanizing:Galvanizing, a process of coating steel with zinc, provides excellent protection against corrosion by creating a sacrificial layer that corrodes instead of the steel.
2. Physical Damage
Physical damage is another major cause of exhaust system deterioration. This can occur due to collisions, road debris, or improper installation.
Common Causes of Physical Damage
- Collisions:Exhaust systems are vulnerable to damage during collisions, as they are often located in exposed areas of the vehicle.
- Road Debris:Objects such as rocks, gravel, or other debris can strike the exhaust system, causing dents, cracks, or punctures.
- Improper Installation:Exhaust systems that are not properly installed or secured can become loose and vibrate, leading to damage over time.
Types of Damage
- Dents:Dents can weaken the exhaust system and restrict the flow of exhaust gases, reducing engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Cracks:Cracks can allow exhaust gases to leak, compromising the vehicle’s emissions and potentially creating a safety hazard.
- Leaks:Leaks can occur at joints or connections, allowing exhaust gases to escape. This can lead to reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and a loud exhaust noise.
Protecting Exhaust Systems from Physical Damage
- Protective Shields:Installing protective shields or skid plates can help deflect road debris and prevent damage to the exhaust system.
- Proper Installation:Ensure that the exhaust system is properly installed and secured to prevent vibration and movement that can lead to damage.
- Regular Inspections:Regularly inspect the exhaust system for any signs of damage, such as dents, cracks, or leaks, and address them promptly.
3. Excessive Heat and Thermal Stress

Exhaust systems are subjected to extreme temperatures, which can weaken components over time. This is especially true for vehicles that operate in hot climates or under heavy loads.
Impact of Extreme Temperatures
- Prolonged Heat Exposure:Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause metal components to soften and lose strength.
- Thermal Cycling:Rapid heating and cooling cycles, such as when driving in cold weather and then stopping the engine, can create thermal stress that weakens the exhaust system.
Strategies for Reducing Thermal Stress
- Heat Shields:Installing heat shields around the exhaust system can help protect it from excessive heat and reduce thermal stress.
- High-Temperature Materials:Using exhaust components made of high-temperature materials, such as stainless steel or titanium, can withstand extreme heat better.
- Proper Engine Maintenance:Ensuring that the engine is properly maintained and operating efficiently can reduce the amount of heat produced, thereby minimizing thermal stress on the exhaust system.
4. Moisture and Condensation

Moisture and condensation can cause significant damage to exhaust systems, especially during cold and humid weather.
How Moisture Enters Exhaust Systems
- Condensation:Moisture can condense inside the exhaust system when hot exhaust gases cool down, creating a corrosive environment.
- Water Ingress:Water can enter the exhaust system through cracks, leaks, or during heavy rain or flooding.
Effects of Condensation
- Corrosion:Condensation creates a moist environment that accelerates the corrosion process, leading to rust formation and damage to metal components.
- Blockages:Condensed water can freeze and block the exhaust system, restricting the flow of exhaust gases and reducing engine performance.
Solutions for Preventing Moisture Buildup
- Exhaust System Design:Exhaust systems should be designed to minimize condensation by allowing moisture to drain away.
- Anti-Condensation Coatings:Applying anti-condensation coatings to the inside of the exhaust system can help prevent moisture buildup.
- Exhaust Heat Wrap:Wrapping the exhaust system with heat wrap can reduce condensation by keeping it warm and preventing rapid cooling.
5. Chemical Attack: What Can Cause Your Exhaust System To Deteriorate Over Time
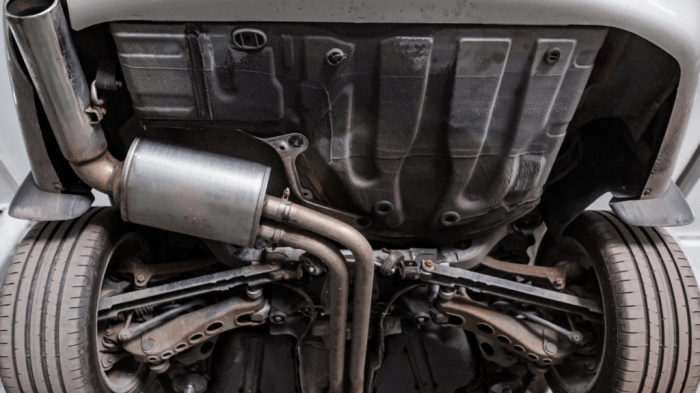
Exhaust systems are exposed to various chemicals that can cause damage and corrosion.
Common Chemicals Causing Damage
- Road Salt:As mentioned earlier, road salt used for de-icing can significantly accelerate corrosion of exhaust systems.
- Cleaning Agents:Harsh cleaning agents used to clean the exterior of vehicles can contain chemicals that can damage the exhaust system if not properly diluted.
- Exhaust Fumes:The exhaust gases themselves contain chemicals that can be corrosive to the exhaust system over time.
Mechanisms of Chemical Damage
- Acidic Attack:Chemicals such as road salt and exhaust fumes can react with metal components, forming acidic compounds that corrode the exhaust system.
- Oxidizing Agents:Certain chemicals, such as cleaning agents, can act as oxidizing agents, promoting the formation of rust.
Recommendations for Protection
- Regular Cleaning:Regularly cleaning the exhaust system can remove chemicals and debris that may cause damage.
- Protective Coatings:Applying protective coatings, such as paint or anti-corrosion sprays, can create a barrier between the metal and chemicals.
- Proper Dilution:Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using cleaning agents to ensure proper dilution and avoid damage to the exhaust system.
Question Bank
What are the signs of a deteriorating exhaust system?
Some of the signs of a deteriorating exhaust system include: increased noise, decreased fuel efficiency, and visible rust or corrosion.
What are the most common causes of exhaust system deterioration?
The most common causes of exhaust system deterioration include: rust and corrosion, physical damage, excessive heat and thermal stress, moisture and condensation, and chemical attack.
How can I prevent exhaust system deterioration?
There are a number of things you can do to prevent exhaust system deterioration, including: avoiding exposure to moisture and corrosive chemicals, protecting the exhaust system from physical damage, and having the exhaust system inspected and serviced regularly.